ZooKeeper终极指南

目录

《ZooKeeper终极指南》
一、ZooKeeper是什么?为什么分布式系统离不开它?
ZooKeeper是一个分布式的、开放源码的分布式应用程序协调服务,是Google的Chubby一个开源的实现,是Hadoop和HBase的重要组件。
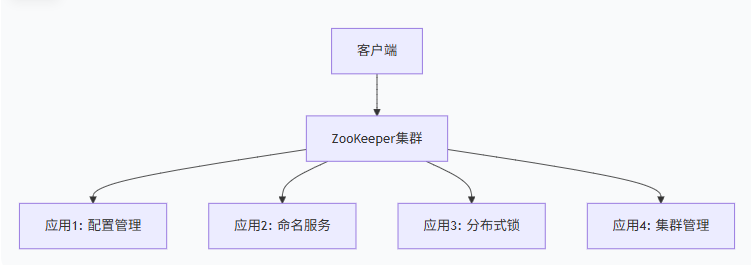
核心功能:
- 配置管理:集中管理集群配置信息
- 命名服务:分布式系统节点命名
- 分布式同步:节点间的数据同步
- 集群管理:节点状态监控和Leader选举
二、ZooKeeper核心概念解析
1. 数据模型:ZNode
ZooKeeper的数据模型采用层次化的树形结构,每个节点称为ZNode。
# 典型的ZNode路径
/app1
/config
/database
/redis
/nodes
/node0001
/node0002ZNode类型:
- 持久节点:永久存在,除非显式删除
- 临时节点:客户端会话结束时自动删除
- 顺序节点:自动在节点名后加上顺序编号
2. 版本机制
每个ZNode都有以下版本信息:
version:数据版本号cversion:子节点版本号aversion:ACL版本号
3. Watcher机制
客户端可以在ZNode上设置监听器,当节点发生变化时,ZooKeeper会向客户端发送通知。
三、ZooKeeper集群架构
集群角色:
| 角色 | 职责 | 数量要求 |
|---|---|---|
| Leader | 处理所有写请求,发起投票 | 1个 |
| Follower | 处理读请求,参与投票 | 至少2个 |
| Observer | 处理读请求,不参与投票 | 可选 |
选举算法:Zab协议
ZooKeeper使用Zab(ZooKeeper Atomic Broadcast)协议保证分布式一致性。
// 简化的选举过程
public class Election {
private long myId;
private long currentLeader;
public void startElection() {
// 1. 每个节点投票给自己
// 2. 交换投票信息
// 3. 选择zxid最大的节点为Leader
// 4. 如果zxid相同,选择serverId最大的
}
}四、ZooKeeper安装与配置
1. 单机模式安装
# 下载解压
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/zookeeper/zookeeper-3.6.3/apache-zookeeper-3.6.3-bin.tar.gz
tar -zxvf apache-zookeeper-3.6.3-bin.tar.gz
cd apache-zookeeper-3.6.3-bin
# 配置
cp conf/zoo_sample.cfg conf/zoo.cfg
./bin/zkServer.sh start2. 集群模式配置
# conf/zoo.cfg
tickTime=2000
dataDir=/var/lib/zookeeper
clientPort=2181
initLimit=5
syncLimit=2
server.1=zk1:2888:3888
server.2=zk2:2888:3888
server.3=zk3:2888:38883. 客户端连接
# 命令行客户端
./bin/zkCli.sh -server localhost:2181
# 常用命令
[zk: localhost:2181] ls /
[zk: localhost:2181] create /test "data"
[zk: localhost:2181] get /test
[zk: localhost:2181] set /test "new data"五、Java客户端实战
1. 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
<version>3.6.3</version>
</dependency>2. 基本操作示例
public class ZooKeeperClient {
private ZooKeeper zk;
private CountDownLatch connectedSignal = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 连接ZooKeeper
public void connect(String hosts) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
zk = new ZooKeeper(hosts, 5000, new Watcher() {
public void process(WatchedEvent we) {
if (we.getState() == Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected) {
connectedSignal.countDown();
}
}
});
connectedSignal.await();
}
// 创建节点
public void create(String path, byte[] data) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
zk.create(path, data, ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
// 读取数据
public String getData(String path) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
byte[] data = zk.getData(path, false, null);
return new String(data, "UTF-8");
}
// 设置监听器
public void watchNode(String path) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
zk.getData(path, new Watcher() {
public void process(WatchedEvent we) {
if (we.getType() == Event.EventType.NodeDataChanged) {
System.out.println("节点数据发生变化: " + path);
}
}
}, null);
}
}3. 分布式锁实现
public class DistributedLock {
private ZooKeeper zk;
private String lockPath;
private String currentPath;
public boolean tryLock() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
// 创建临时顺序节点
currentPath = zk.create(lockPath + "/lock-", null,
ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL);
// 获取所有锁节点并排序
List<String> children = zk.getChildren(lockPath, false);
Collections.sort(children);
// 判断当前节点是否是最小的
String smallest = children.get(0);
return currentPath.endsWith(smallest);
}
public void unlock() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
zk.delete(currentPath, -1);
}
}六、典型应用场景
1. 配置管理
public class ConfigManager {
private Map<String, String> config = new HashMap<>();
public void init() throws Exception {
// 监听配置节点
zk.getData("/app/config", new Watcher() {
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
if (event.getType() == Event.EventType.NodeDataChanged) {
loadConfig(); // 重新加载配置
}
}
}, null);
loadConfig();
}
private void loadConfig() throws Exception {
byte[] data = zk.getData("/app/config", false, null);
// 解析配置并更新内存
config = parseConfig(new String(data));
}
}2. 服务发现
public class ServiceDiscovery {
private List<String> servers = new ArrayList<>();
public void watchServices() throws Exception {
// 监听服务节点
zk.getChildren("/services", new Watcher() {
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
if (event.getType() == Event.EventType.NodeChildrenChanged) {
updateServers(); // 更新服务列表
}
}
});
updateServers();
}
private void updateServers() throws Exception {
List<String> children = zk.getChildren("/services", false);
servers = children.stream()
.map(path -> getServerData("/services/" + path))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}3. Leader选举
public class LeaderElection {
private String currentPath;
private boolean isLeader = false;
public void participate() throws Exception {
// 创建临时顺序节点
currentPath = zk.create("/election/node-", null,
ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL);
// 监听前一个节点
watchPreviousNode();
}
private void watchPreviousNode() throws Exception {
List<String> nodes = zk.getChildren("/election", false);
Collections.sort(nodes);
int currentIndex = nodes.indexOf(currentPath);
if (currentIndex == 0) {
becomeLeader(); // 成为Leader
} else {
String previousNode = nodes.get(currentIndex - 1);
// 监听前一个节点
zk.exists("/election/" + previousNode, new Watcher() {
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
if (event.getType() == Event.EventType.NodeDeleted) {
watchPreviousNode(); // 重新检查
}
}
});
}
}
private void becomeLeader() {
isLeader = true;
System.out.println("成为Leader节点");
}
}七、最佳实践与性能优化
1. 配置优化
# zoo.cfg 优化配置
tickTime=2000
initLimit=10
syncLimit=5
maxClientCnxns=60
minSessionTimeout=4000
maxSessionTimeout=40000
autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
autopurge.purgeInterval=12. 监控指标
| 指标 | 说明 | 正常范围 |
|---|---|---|
| zk_avg_latency | 平均响应时间 | < 10ms |
| zk_outstanding_requests | 堆积请求数 | < 10 |
| zk_znode_count | ZNode数量 | < 10万 |
| zk_watch_count | Watch数量 | < 5万 |
3. 常见问题排查
# 查看服务器状态
echo stat | nc localhost 2181
# 查看连接详情
echo cons | nc localhost 2181
# 查看Watch统计
echo wchs | nc localhost 2181
# 查看节点详情
echo dump | nc localhost 2181八、ZooKeeper vs 其他协调服务
| 特性 | ZooKeeper | etcd | Consul |
|---|---|---|---|
| 一致性算法 | Zab | Raft | Raft |
| 读写性能 | 写慢读快 | 读写均衡 | 读写均衡 |
| Watch机制 | 一次性监听 | 长连接监听 | 长连接监听 |
| 健康检查 | 会话机制 | 心跳检查 | 多种检查方式 |
| 适用场景 | Hadoop生态 | Kubernetes | 服务发现 |
九、总结
ZooKeeper作为分布式系统的基石,提供了可靠的协调服务。通过本文的学习,你应该掌握:
- ZooKeeper的核心概念和数据模型
- 集群架构和选举机制
- Java客户端编程实践
- 典型应用场景实现
- 性能优化和监控方法
学习建议:
- 搭建ZooKeeper集群进行实践
- 阅读Zab协议论文深入了解一致性算法
- 结合Dubbo、Kafka等框架学习实际应用
ZooKeeper虽然现在有etcd、Consul等竞争对手,但在大数据领域仍然有着不可替代的地位!
每天进步一点点!
