数据结构邻接表

目录

【数据结构——邻接表】
引入
上篇对邻接矩阵进行了实现,这篇要实现的是邻接表:
每个顶点维护一个链表,存储其相邻顶点。
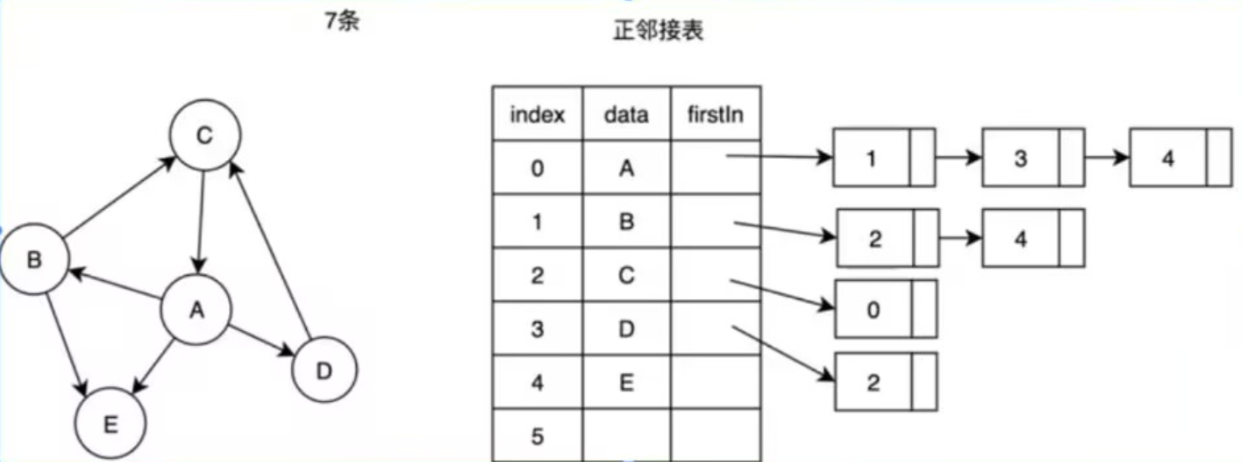
头文件
结构组成
//邻接表的边结构
typedef struct arcEdge{
int no; //边的顶点编号,no始终存储弧头(边的终点)
//在有向图中被指向的顶点称为弧头(可以理解为是箭头指向的,所以称弧头)
//无向图中no的含义与有向图一致,表示该边连接的另一个顶点的编号(即相邻顶点)
int weight; //该边的权值
struct arcEdge* next; //指向下一条边结构
}ArcEdge;
//顶点结构
typedef struct {
int no; //顶点编号
char* show; //顶点显示内容(如A、B…)
ArcEdge* firstEdge; //该顶点指向其他顶点的边的链表首地址(边存在链表中)
//所以边结构里面的变量no存储的是该顶点指向的其他顶点(弧头)
}ArcNode; //Arc:有向图中的单向边,Edge:无向图中的边
//邻接表来表示图
typedef struct {
ArcNode* node; //图中顶点的集合(顶点是用数组存储的)
int* visited; //标记遍历过的顶点
int nodeNum; //图的顶点个数
int edgeNum; //边的个数
int directed; //当前图是否有向
}AGraph;具体功能
//产生一个n个顶点的邻接表
AGraph* createAGraph(int n);
//释放邻接表
void releaseAGraph(AGraph* graph);
//初始化邻接表
void initAGraph(AGraph* graph,const char* names[], int num, int directed);
//在邻接表graph中,添加一条从顶点x指向顶点y且权值为w的边
void addAGraph(AGraph* graph, int x, int y, int w);
//访问当前顶点
void visitAGraphNode(const ArcNode*node);
void DFS_AGraph(const AGraph* graph, int v);
void BFS_AGraph(const AGraph* graph, int v);
//重置,防止连续遍历时受干扰
void resetAGraphVisited(AGraph* graph);- 在功能实现之前先理清ArcEdge结构里面的no与next的区别:
no(弧尾)与next的区别
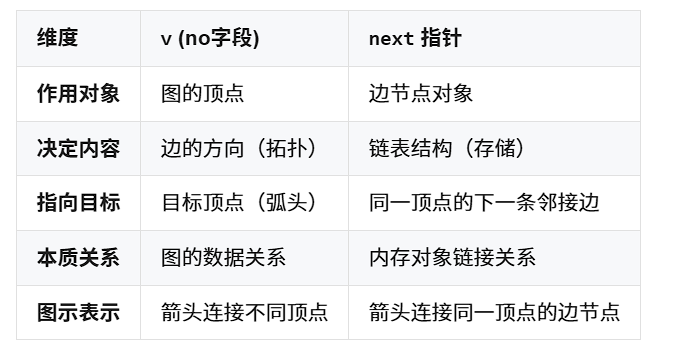
- 两者在进行边的添加操作时可以看成两部分:
no主要用于表示与所添加的边相关联的顶点的编号;next主要用来表示这个新增的边在存储边的链表中所处的节点位置与插入逻辑的实现。
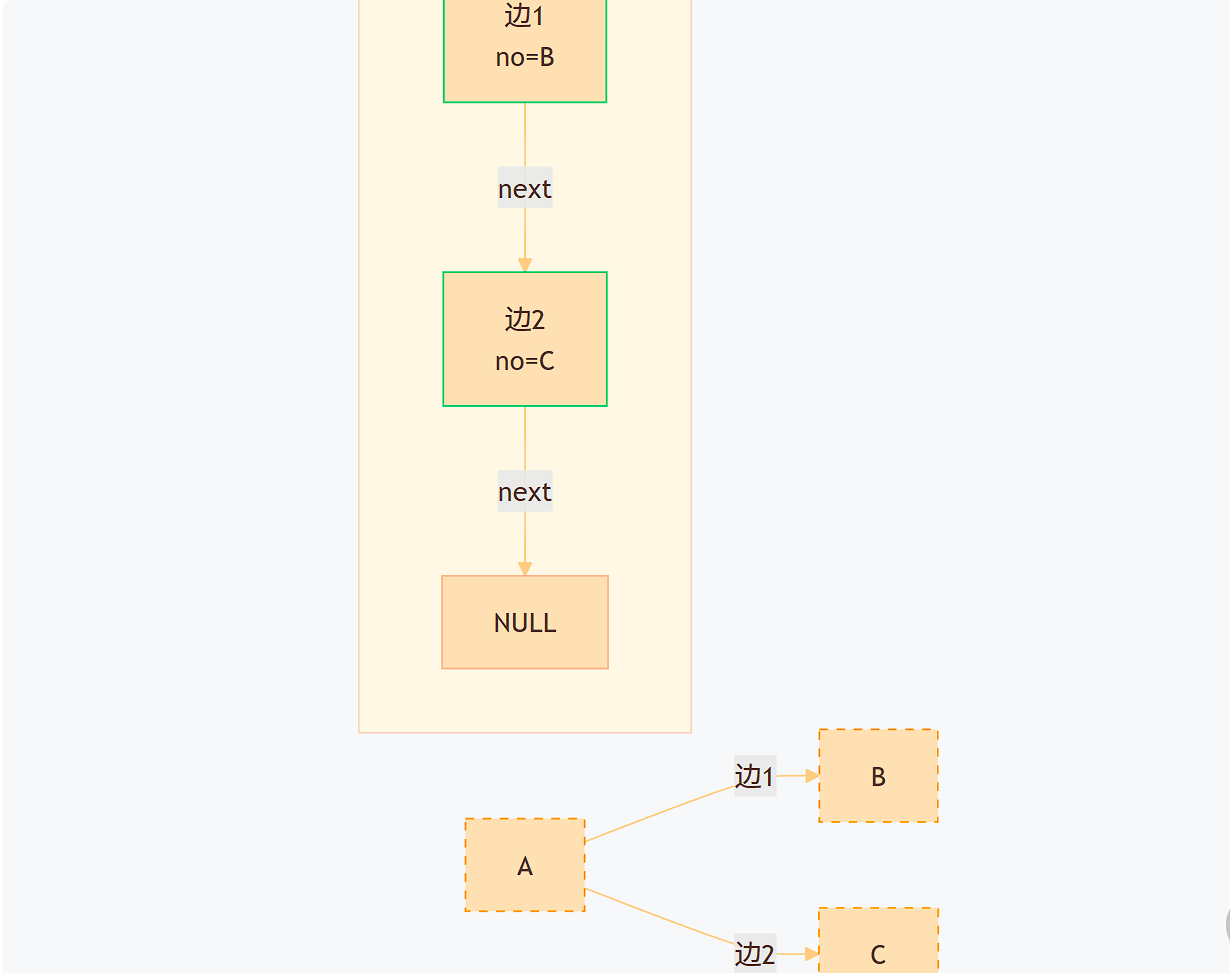
新边是通过头插法实现的,如下图edge->next指向原第一条边:
功能实现
产生邻接表
AGraph* createAGraph(int n) {
AGraph* graph = (AGraph*)malloc(sizeof(AGraph));
if (graph == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
graph->directed = 0;
graph->edgeNum = 0;
graph->nodeNum = n;
graph->node = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
graph->visited = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
if (graph->node == NULL || graph->visited == NULL) {
free(graph);
return NULL;
}
memset(graph->node, 0,sizeof(ArcNode)*n);
memset(graph->visited, 0,sizeof(int)*n);
return graph;
}初始化
void initAGraph(AGraph* graph,const char* name[], int num, int directed) {
graph->directed = directed;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
graph->node[i].no = i;
graph->node[i].show = (char*)name[i];
graph->node[i].firstEdge = NULL;
}
}新增边
static ArcEdge* createArcEdge(int v, int w) {
ArcEdge* edge = (ArcEdge*)malloc(sizeof(ArcEdge));
if (edge == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
edge->no = v;
edge->weight = w;
edge->next = NULL;
return edge;
}
void addAGraph(AGraph* graph, int x, int y, int w) {
if (x < 0 || x >= graph->nodeNum || y < 0 || y >= graph->nodeNum) {
return;
}
if (x == y) return;
ArcEdge* edge = createArcEdge(y, w);
edge->next = graph->node[x].firstEdge; //理解成两个不同区域的数据整理(点记点的数据,边记边)
//将新边添加到顶点x的邻接链表中,隐式声明了这条边的起点(弧尾)是x
graph->node[x].firstEdge = edge;
graph->edgeNum++;
if (graph->directed == 0) {
edge = createArcEdge(x, w);
edge->next = graph->node[y].firstEdge;
graph->node[y].firstEdge=edge;
graph->edgeNum++;
}
//可以理解为弧尾是谁就将新边添加到谁的边链表中(无向添加两次)
}访问顶点
void visitAGraphNode(const ArcNode* node) {
printf("\t%s", node->show);
}深搜
void DFS_AGraph(const AGraph* graph, int v) {
ArcEdge* p;
graph->visited[v] = 1; //先标记再访问
visitAGraphNode(&graph->node[v]);
p = graph->node[v].firstEdge; // p指向顶点v的第一条邻接边
while (p) { // 检查该边指向的顶点是否被访问过
if (graph->visited[p->no] == 0) {
DFS_AGraph(graph, p->no);
}
p = p->next;
}
}重置访问标记
void resetAGraphVisited(AGraph* graph) {
memset(graph->visited, 0, sizeof(int) * graph->nodeNum);
}广搜
void BFS_AGraph(const AGraph* graph, int v) {
int* que = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * graph->nodeNum);
int front = 0, rear = 0;
ArcEdge* p;
int cur;
rear = (rear + 1) % graph->nodeNum;
que[rear] = v;
graph->visited[v] = 1; //入队即一定会被访问,所以一入对就标记
while (front != rear) {
front = (front + 1) % graph->nodeNum;
cur = que[front];
visitAGraphNode(&graph->node[cur]);
p = graph->node[cur].firstEdge; //传入链表头给p
while (p) {
if (graph->visited[p->no] == 0) {
rear = (rear + 1) % graph->nodeNum;
que[rear] = p->no;
graph->visited[p->no] = 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
free(que);
}实现对象: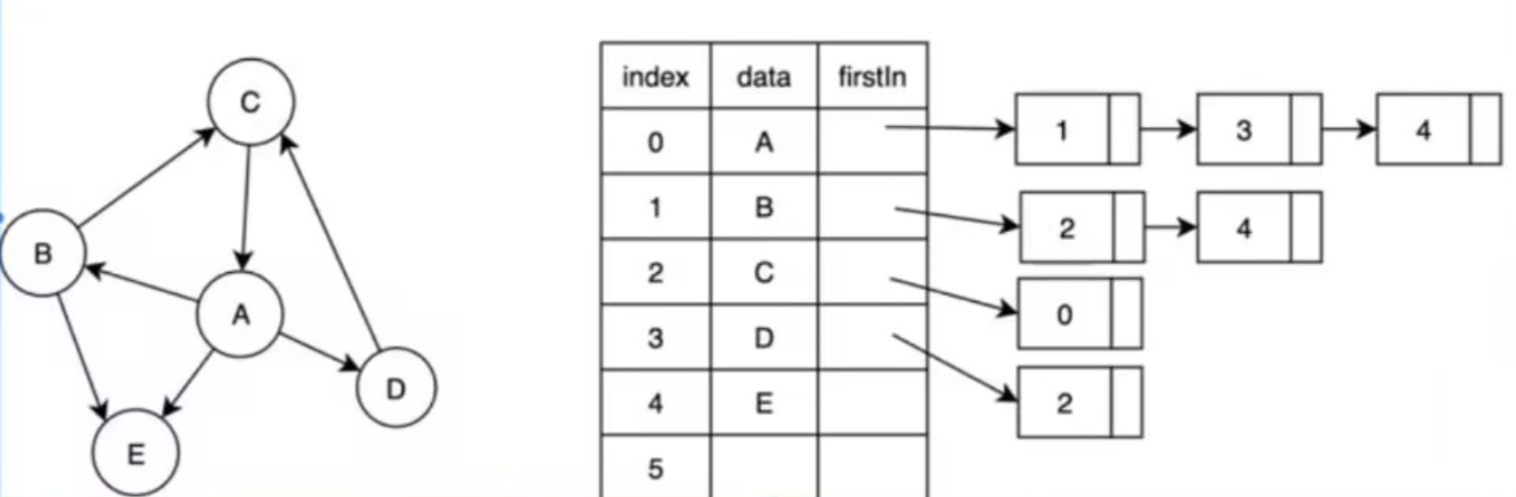
功能调用
static void setupGraph(AGraph* graph) {
const char* name[] ={"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"};
initAGraph(graph, name, sizeof(name) / sizeof(name[0]), 1);
addAGraph(graph, 0, 4, 1);
addAGraph(graph, 0, 3, 1);
addAGraph(graph, 0, 1, 1);
addAGraph(graph, 1, 4, 1);
addAGraph(graph, 1, 2, 1);
addAGraph(graph, 2, 0, 1);
addAGraph(graph, 3, 2, 1);
}
int main() {
int n = 5;
AGraph* graph = createAGraph(n);
setupGraph(graph);
printf("图的边数: %d\n", graph->edgeNum);
printf("图的深度遍历:");
DFS_AGraph(graph, 0);
printf("\n图的广度遍历:");
resetAGraphVisited(graph);
BFS_AGraph(graph, 0);
return 0;
}
