Python3练习题


Python3练习题
[ VibeCoding·九月创作之星挑战赛
10w+人浏览
1.4k人参与
VibeCoding·九月创作之星挑战赛
10w+人浏览
1.4k人参与
 ](
)
](
)
上一节中全面讲解了基础知识,为了巩固知识点,当然最好的方法就是练习了。
练习 1:变量类型转换与算术运算
需求:接收用户输入的两个数字(可能是整数或字符串格式),转换为浮点数后计算 “幂运算、整除、取余” 结果,并打印类型信息。
def main():
num1_str = input("first number:")
num2_str = input("second number:")
fnum1 = float(num1_str)
fnum2 = float(num2_str)
pow_result = fnum1 ** fnum2
div_result = fnum1 // fnum2
mod_result = fnum1 % fnum2
# 打印结果与类型
print(f"\n{fnum1} 的 {fnum2} 次幂:{pow_result},类型:{type(pow_result)}")
print(f"{fnum1} 整除 {fnum2}:{div_result},类型:{type(div_result)}")
print(f"{fnum1} 取余 {fnum2}:{mod_result},类型:{type(mod_result)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()结果: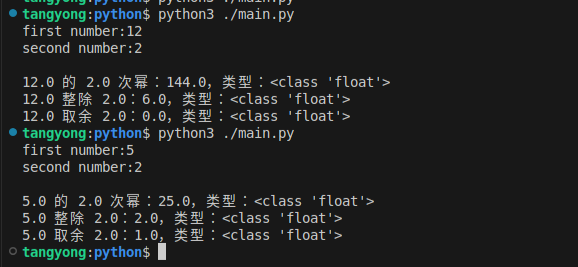
练习 2:多条件判断与循环
需求:遍历 1~20 的整数,按以下规则分类打印:
能被 3 和 5 同时整除:打印 “[数字] 是 3 和 5 的倍数”
能被 3 整除:打印 “[数字] 是 3 的倍数”
能被 5 整除:打印 “[数字] 是 5 的倍数”
其余数字:打印 “[数字] 不是目标倍数”
def main():
for i in range(1,21):
if i % 3 == 0 and i %5 == 0:
print(f"[{i}] 是 3 和 5 的倍数")
elif i %3 == 0:
print(f"[{i}] 是 3 的倍数")
elif i % 5 == 0:
print(f"[{i}] 是 5 的倍数")
else:
print(f"[{i}] 不是目标倍数")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()结果: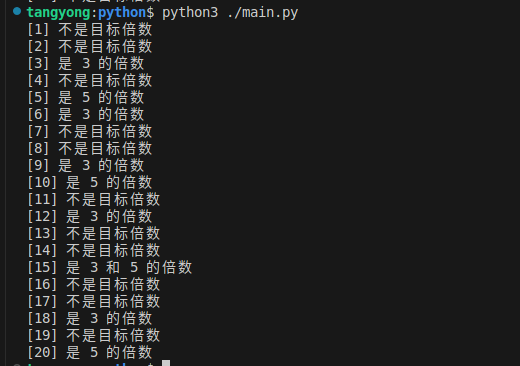
练习 3:可变参数与多返回值
需求:定义一个函数,接收 “固定参数(商品基础价)+ 可变位置参数(折扣比例列表)+ 可变关键字参数(额外费用,如运费、服务费)”,计算并返回 “最低折扣价、最高折扣价、最终总价(基础价 × 折扣 + 额外费用总和)”。
def calculate_price(base_price,*discount,**extra_fees):
# 计算最低/最高折扣价
min_discount_price = base_price * min(discount)
max_discount_price = base_price * max(discount)
# 计算额外费用总和(关键字参数的value求和)
total_extra = sum(extra_fees.values())
# 计算最终总价(取最低折扣价+额外费用)
final_price = min_discount_price + total_extra
# 多返回值(实际返回元组)
return min_discount_price, max_discount_price, final_price
if __name__ == "__main__":
min_p,max_p,final_p = calculate_price(100,0.8,0.9,ship = 10,servce=5)
# 打印结果
print(f"基础价:100 元")
print(f"最低折扣价:{min_p:.2f} 元")
print(f"最高折扣价:{max_p:.2f} 元")
print(f"最终总价(最低折扣+额外费用):{final_p:.2f} 元")结果: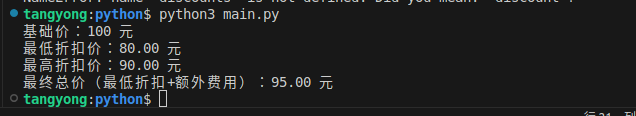
练习 4:函数装饰器
需求:定义一个 “计时装饰器”,用于统计任意函数的执行时间,并打印 “函数名、参数、返回值、执行耗时”。
import time
import time
# 定义计时装饰器
def time_decorator(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 执行前:记录开始时间
start_time = time.time()
# 调用原函数,获取返回值
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
# 执行后:计算耗时,打印信息
end_time = time.time()
cost_time = (end_time - start_time) * 1000 # 转换为毫秒
print(f"\n=== 函数执行报告 ===")
print(f"函数名:{func.__name__}")
print(f"位置参数:{args}")
print(f"关键字参数:{kwargs}")
print(f"返回值:{result}")
print(f"执行耗时:{cost_time:.2f} 毫秒")
return result
return wrapper
# 使用装饰器装饰目标函数(计算1到n的和)
@time_decorator
def sum_to_n(n):
total = 0
for i in range(1, n+1):
total += i
return total
if __name__ == "__main__":
sum_result = sum_to_n(100000)
print(f"\n1到100000的和:{sum_result}")
sum_result = sum_to_n(1000000)
print(f"\n1到100000的和:{sum_result}")结果: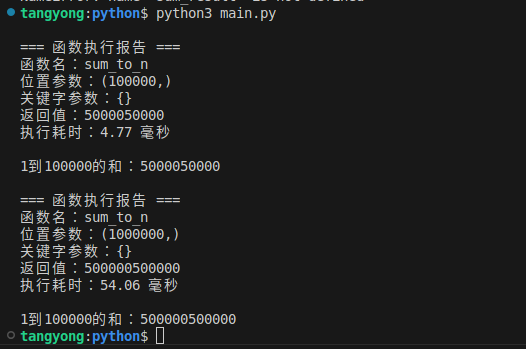
练习 5:列表与字典操作
需求:
用列表存储 5 个学生的姓名和成绩(格式:["张三:90", "李四:85", ...])
将列表转换为字典(键:姓名,值:成绩)
筛选出成绩≥85 的学生,按成绩降序排序并打印def main():
students = ["张三:88","李四:66","王五:99","赵六:66","二蛋:85"]
#2.转换为字典
score_dict = {}
for text in students:
key,value = text.split(":")
score_dict[key] = int(value)
high_score_student = [(name,score) for name,score in score_dict.items() if score >= 85]
print(high_score_student)
sorted_student = sorted(high_score_student,key = lambda x :x[1],reverse = True)
print(sorted_student)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()结果: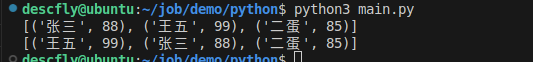
练习 6:集合运算
需求:已知两个集合(A:数学满分学生,B:语文满分学生),计算 “两科都满分(交集)、至少一科满分(并集)、仅数学满分(差集)” 的学生名单。
def main():
# 定义两个集合
math_full = {"张三", "李四", "赵六"} # 数学满分
chinese_full = {"李四", "王五", "孙七"} # 语文满分
# 集合运算
both_full = math_full & chinese_full # 交集:两科都满分
any_full = math_full | chinese_full # 并集:至少一科满分
only_math = math_full - chinese_full # 差集:仅数学满分
# 打印结果
print("数学满分学生:", math_full)
print("语文满分学生:", chinese_full)
print("两科都满分学生:", both_full)
print("至少一科满分学生:", any_full)
print("仅数学满分学生:", only_math)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()结果: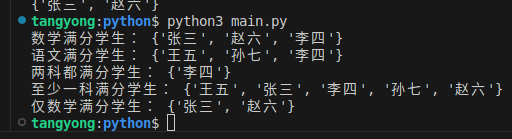
练习 7:字符串格式化与常用方法
需求:接收用户输入的 “姓名、年龄、身高(cm)”,按以下格式输出个人信息,并统计 “姓名长度、身高是否≥170cm”:
def main():
# 接收用户输入
name = input("请输入姓名:")
age_str = input("请输入年龄:")
height_str = input("请输入身高(cm):")
# 数据处理:年龄转整数,身高转整数
age = int(age_str)
height = int(height_str)
# 字符串格式化(f-string)
info = f"""【个人信息卡】
姓名:{name}(长度:{len(name)}字)
年龄:{age}岁(明年:{age+1}岁)
身高:{height}cm(是否达标:{'是' if height >= 170 else '否'})"""
# 打印结果
print(info)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()结果: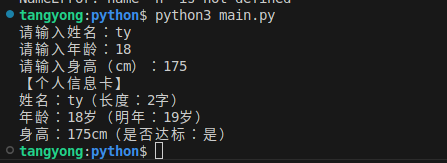
练习 8:文件读写与内容统计
需求:
向 “student.txt” 文件写入 3 行学生信息(格式:姓名,年龄,成绩)
读取文件内容,统计 “平均成绩、最高成绩及对应姓名”
将统计结果追加到文件末尾
def file_read_write_demo():
# 1. 写入文件(覆盖模式,若文件不存在则创建)
with open("student.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("张三,20,90\n")
f.write("李四,19,85\n")
f.write("赵六,21,95\n")
print("已写入学生信息到 student.txt")
# 2. 读取文件并统计
names = []
scores = []
with open("student.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip() # 去除换行符和空格
if not line:
continue # 跳过空行
name, age_str, score_str = line.split(",")
names.append(name)
scores.append(int(score_str))
# 计算统计结果
avg_score = sum(scores) / len(scores)
max_score = max(scores)
max_score_name = names[scores.index(max_score)]
# 3. 追加统计结果到文件
with open("student.txt", "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("\n=== 成绩统计结果 ===\n")
f.write(f"平均成绩:{avg_score:.1f}\n")
f.write(f"最高成绩:{max_score}({max_score_name})\n")
print("已追加统计结果到 student.txt")
# 验证:读取文件全部内容并打印
with open("student.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
content = f.read()
print("\n文件全部内容:")
print(content)
# 调用函数
file_read_write_demo()结果: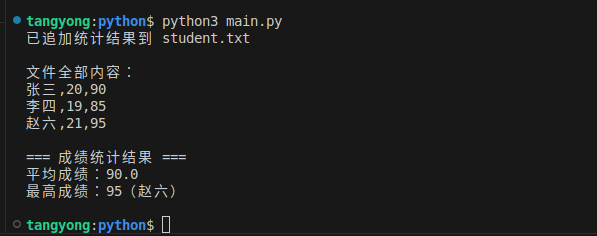
练习 9:类的继承与多态
需求:
定义父类 “Animal”,包含 “name” 属性和 “make_sound” 方法(纯虚函数风格)
定义子类 “Dog”“Cat”“Bird”,重写 “make_sound” 方法(分别输出 “汪汪”“喵喵”“叽叽”)
定义函数 “animal_sound_show”,接收任意 Animal 对象,调用其 “make_sound” 方法(多态)
class Animal:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name # 公开属性
def make_sound(self):
# 父类方法:子类需重写
raise NotImplementedError("子类必须重写 make_sound 方法")
# 子类1:Dog
class Dog(Animal):
def make_sound(self):
print(f"{self.name} 叫:汪汪汪!")
# 子类2:Cat
class Cat(Animal):
def make_sound(self):
print(f"{self.name} 叫:喵喵喵!")
# 子类3:Bird
class Bird(Animal):
def make_sound(self):
print(f"{self.name} 叫:叽叽叽!")
# 多态函数:接收任意Animal子类对象
def animal_sound_show(animal):
if isinstance(animal, Animal): # 检查是否为Animal类型
animal.make_sound()
else:
print("不是有效的Animal对象!")
# 测试:创建对象并调用多态函数
dog = Dog("大黄")
cat = Cat("小白")
bird = Bird("啾啾")
animal_sound_show(dog)
animal_sound_show(cat)
animal_sound_show(bird)
# 测试无效对象
animal_sound_show("不是动物")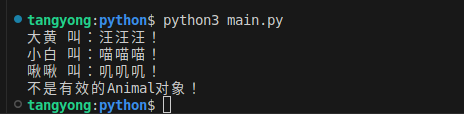
练习 10:特性(property)与访问控制
需求:定义 “Person” 类,用 “特性” 控制 “age” 属性:
年龄必须是 0~150 的整数,否则报错
提供 “get_age”(获取年龄)和 “set_age”(设置年龄)的逻辑,外部通过 “p.age” 直接访问
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
# 初始化时调用setter,确保年龄合法
self.age = age
# 特性:getter(获取年龄)
@property
def age(self):
return self._age # _age 是约定的私有变量
# 特性:setter(设置年龄,带验证)
@age.setter
def age(self, value):
# 验证:必须是整数,且在0~150之间
if not isinstance(value, int):
raise TypeError("年龄必须是整数!")
if value < 0 or value > 150:
raise ValueError("年龄必须在 0~150 之间!")
self._age = value
# 测试:正常情况
p1 = Person("张三", 25)
print(f"{p1.name} 的年龄:{p1.age}")
# 测试:修改年龄(合法)
p1.age = 30
print(f"{p1.name} 修改后的年龄:{p1.age}")
# 测试:非法情况(触发异常,可注释后运行)
# p2 = Person("李四", "20") # 类型错误
# p3 = Person("王五", 200) # 值错误结果: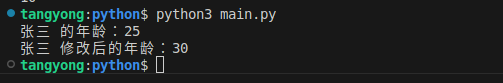
练习 11:自定义模块调用
需求:
创建自定义模块 “math_tools.py”,包含 “add(加法)、multiply(乘法)、is_prime(判断质数)” 三个函数
在主脚本中导入该模块,调用函数并测试
步骤 1:创建模块文件 “math_tools.py”
# math_tools.py(自定义模块)
def add(a, b):
"""加法运算"""
return a + b
def multiply(a, b):
"""乘法运算"""
return a * b
def is_prime(n):
"""判断n是否为质数(质数:大于1的整数,仅能被1和自身整除)"""
if n <= 1:
return False
if n == 2:
return True
if n % 2 == 0:
return False
# 检查3到sqrt(n)的奇数
for i in range(3, int(n**0.5) + 1, 2):
if n % i == 0:
return False
return True步骤 2:主脚本调用模块
# 主脚本 main.py
# 导入自定义模块(三种方式任选)
import math_tools as mt
from math_tools import is_prime
# 测试加法
print("3 + 5 =", mt.add(3, 5))
# 测试乘法
print("4 × 6 =", mt.multiply(4, 6))
# 测试质数判断
test_nums = [7, 12, 17, 20]
for num in test_nums:
print(f"{num} 是质数吗?", is_prime(num))结果: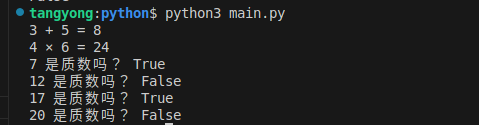
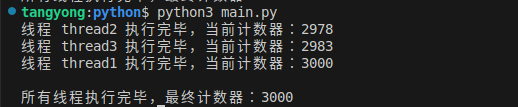
练习 12:多线程与锁同步
需求:创建 3 个线程,共享 “计数器” 变量,每个线程对计数器累加 1000 次,用锁确保计数器最终结果正确(避免竞态条件)。
import threading
import time
num =0
lock = threading.Lock()
def increment_counter(thread_name):
global num
for _ in range(1000):
with lock:
num+=1
time.sleep(0.001)
print(f"线程 {thread_name} 执行完毕,当前计数器:{num}")
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=increment_counter,args=("thread1",))
thread2 = threading.Thread(target=increment_counter,args=("thread2",))
thread3 = threading.Thread(target=increment_counter,args=("thread3",))
thread1.start()
thread2.start()
thread3.start()
# 等待所有线程结束
thread1.join()
thread2.join()
thread3.join()
print(f"\n所有线程执行完毕,最终计数器:{num}")结果: